Strength of concrete is its resistance to rupture. It may be measured in number of ways, such as strength in compression, in tension, in shear or in flexure.
When concrete fails under a compressive load, the failure is essential due to crusting failure and shear failure. The mechanics of failure is a complex phenomenon.
It can be assumed that the concrete in resisting failure, generate both cohesion and internal friction which is related to more or less a single parameter i.e. w/c ratio.
For a given cement and acceptable aggregates, the strength that may be developed by workable, properly placed mixture of cement. aggregate and water is influenced by
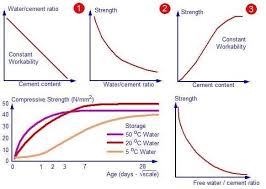
(1) Ratio of cement to mixing water.
(2) Ratio of cement to aggregate.
(3) Grading, surface texture, shape, strength and stiffness of aggregate particles.
(4) Maximum size of aggregate.
w/c ratio primarily affects the strength, whereas other factors indirectly affects it by affecting w/c ratio.