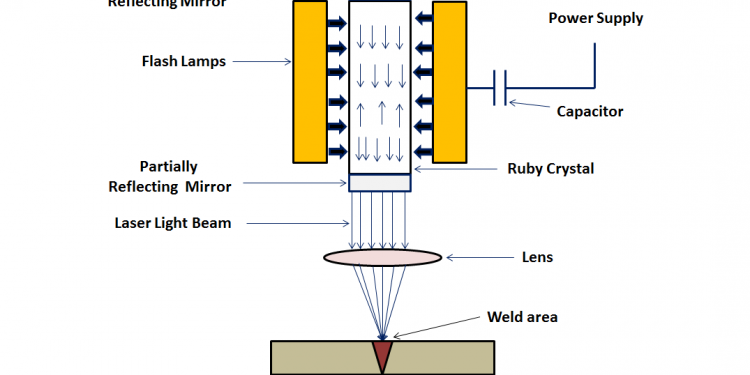
Laser (Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation) welding:
In this method, bombardment of an atom by a proton of adequate energy (while in excited state) stimulates it to emit another proton and thus augment the one bombarding it.
This gives rise to stimulated emission (which synchronous with the inducing radiation in direction, phase and wavelength) and amplifies the incident radiation.
In a matter of milliseconds, a laser beam is built, amplified (by bouncing the light back and forth between the reflecting surfaces on the ends of a crystal) till the stored energy is built up to a critical limit.
A portion of it bursts through the partially reflecting surface, and is focused by a system of optical lenses to a tiny spot (less than 0.25 mm in size) on the work piece.
The energy concentration on this tiny spot becomes very high which can be used for welding job. Laser is effectively used in the welding of chromium, nickel, aluminum, tungsten, titaniumetc.
The salient features of this process are :
(a) Low energy requirement.
(b) Possibility of both spot and seam welding.
(c)Facility for micro miniature welding
The disadvantages include high cost, limited average power, low efficiency and difficulty in controlling the characteristics of the laser beam.
However, laser welding has already gained a prominent place in the welding of micro equipments.